Yana Jin 靳颜蔚 |
|
I am a second-year MS student in Biostatistics at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health. My research focuses on developing and applying machine learning and statistical modeling approaches to improve clinical decision-making and public health outcomes. I work as a Research Assistant with Dr. Feng Xie (UMN Surgery) on emergency sepsis prediction models using data from over 2 million emergency department visits, and with Dr. Xiao Zang (UMN Public Health) on projects related to drug overdose intervention modeling. Previously, I received my Bachelor degree from Peking University in 2022 and worked at the Hong Kong Centre for Cerebro-cardiovascular Health Engineering (COCHE) on cuff-less blood pressure estimation advised by Prof. Yuan-Ting Zhang. |
News |
|
PublicationsMy research focuses on E-health, disease modeling, and the application of machine learning and statistical methods to improve healthcare outcomes. |
|
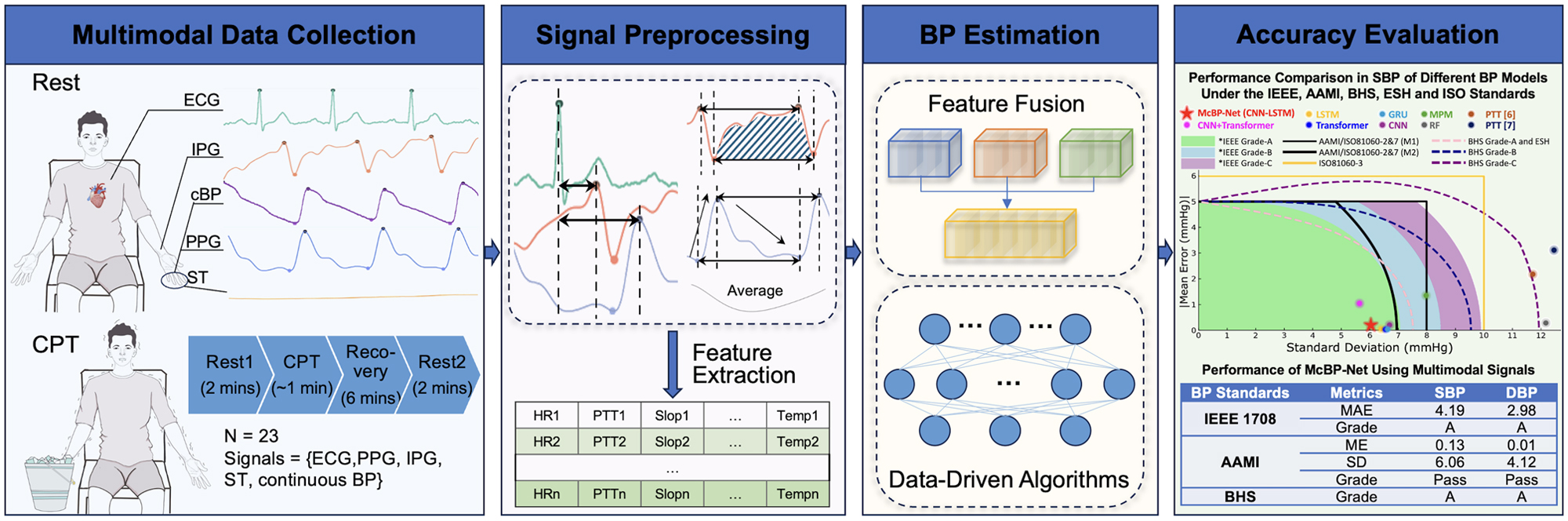
Dynamic Beat-to-Beat Measurements of Blood Pressure Using Multimodal Physiological Signals and a Hybrid CNN-LSTM ModelTing Xiang*, Yanwei Jin*, Zijun Liu, Lei Clifton, David A. Clifton, Yiming Zhang IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2025 paper / Multimodal McBP-Net: hybrid CNN-LSTM for continuous beat-to-beat BP estimation from PPG, ECG, IPG, and skin temperature. Achieves MAE of 4.19 and 2.98 mmHg for SBP/DBP. Published in IEEE JBHI. |
|
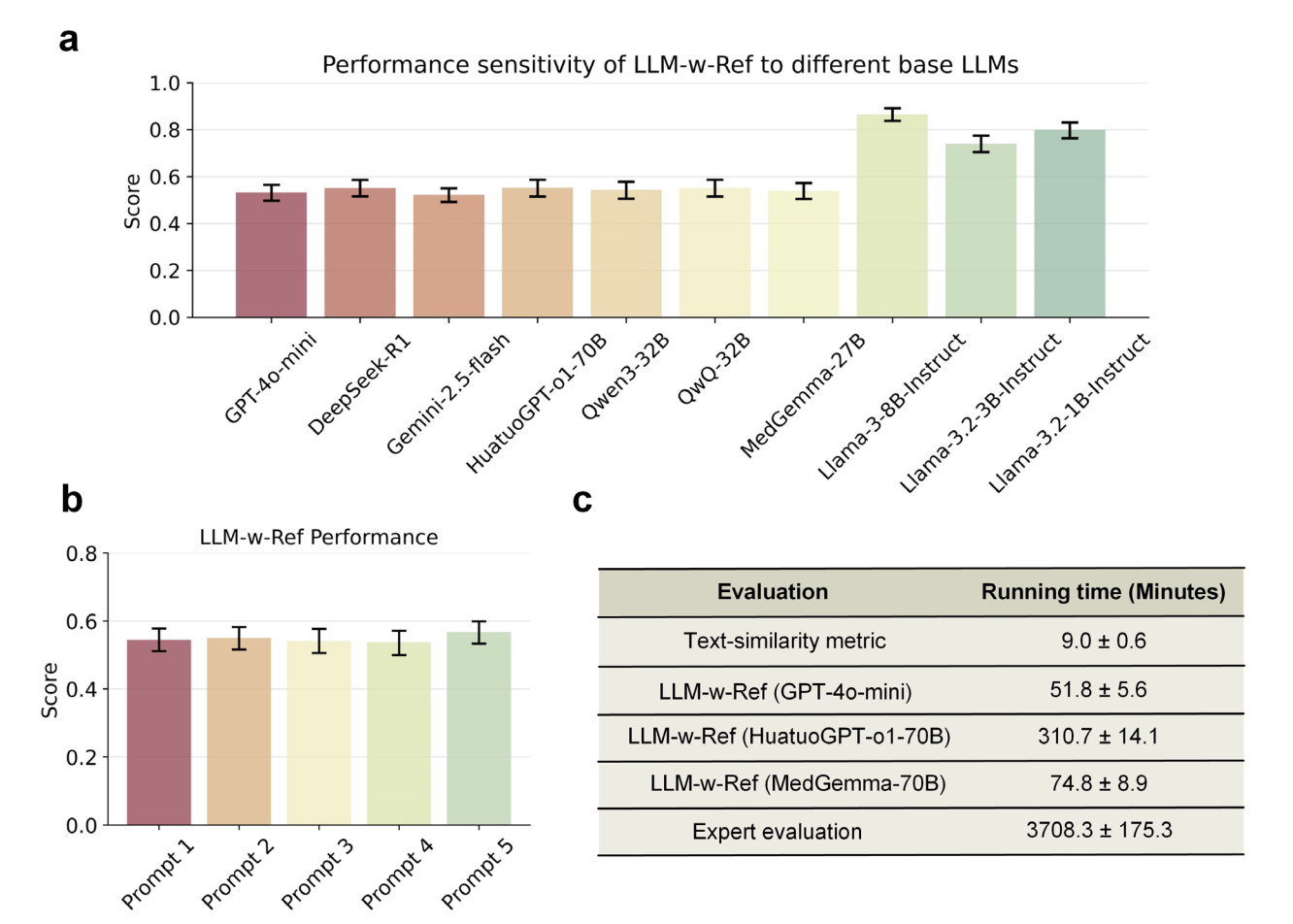
Automating expert-level medical reasoning evaluation of large language modelsShuang Zhou, Wenya Xie, Jiaxi Li, Zaifu Zhan, Meijia Song, Han Yang, Cheyenna Espinoza, Lindsay Welton, Xinnie Mai, Yanwei Jin, Zidu Xu, Yuen-Hei Chung, Yiyun Xing, Meng-Han Tsai, Emma Schaffer, Yucheng Shi, Ninghao Liu, Zirui Liu, Rui Zhang npj Digital Medicine, 2025 paper / MedThink-Bench: 500-question benchmark for assessing LLMs’ medical reasoning with expert rationales. Our LLM-w-Ref framework showed smaller models (MedGemma-27B) can surpass larger proprietary ones (OpenAI-o3). |
|
Model Training Method, Physiological Indicator Detection Method, Apparatus, and Electronic DeviceHenjie Chen, Liangyi Lyu, Lingfeng Li, Yanwei Jin CN Patent CN119441860A, 2025 **Patent** for a model training method, physiological indicator detection method, apparatus, and electronic device. This patent covers innovative approaches for training machine learning models and detecting physiological indicators using wearable devices and sensor technologies. Patent Number: **CN119441860A**, Application Number: CN202411352734.6, granted by the China National Intellectual Property Administration. |
|
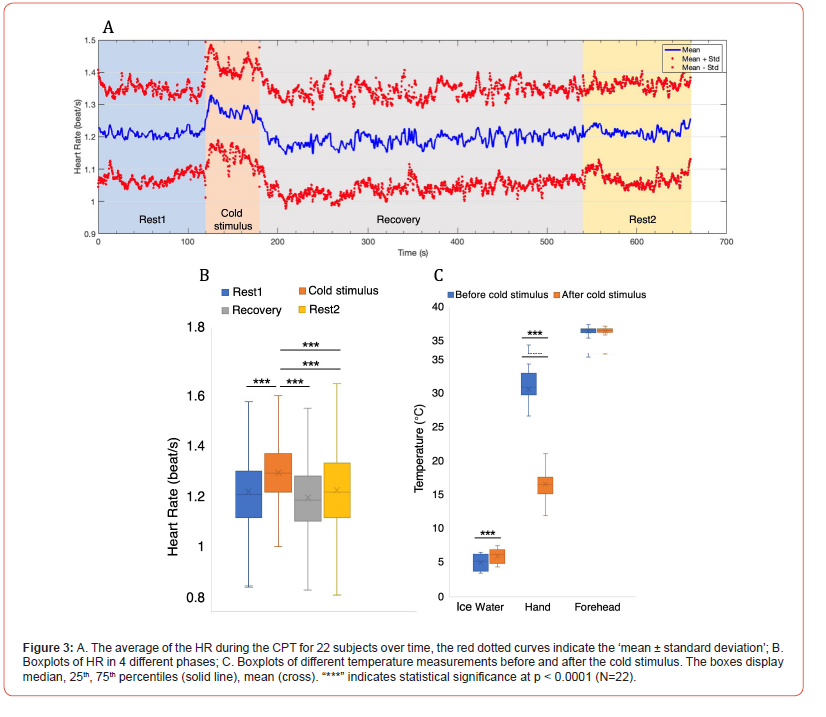
Wearables Cardiovascular Monitoring: Effects of Cold Pressor Test on Heart Rates Estimated From ECG, PPG and IPG SignalsT Xiang, ZJ Liu, YW Jin, N Ji and YT Zhang* Online Journal of Robotics & Automation Technology, 2024 paper / Cold pressor test effects on heart rate and HRV in 22 subjects. Cold exposure significantly increased HR (p<0.001) and decreased HRV. |
|
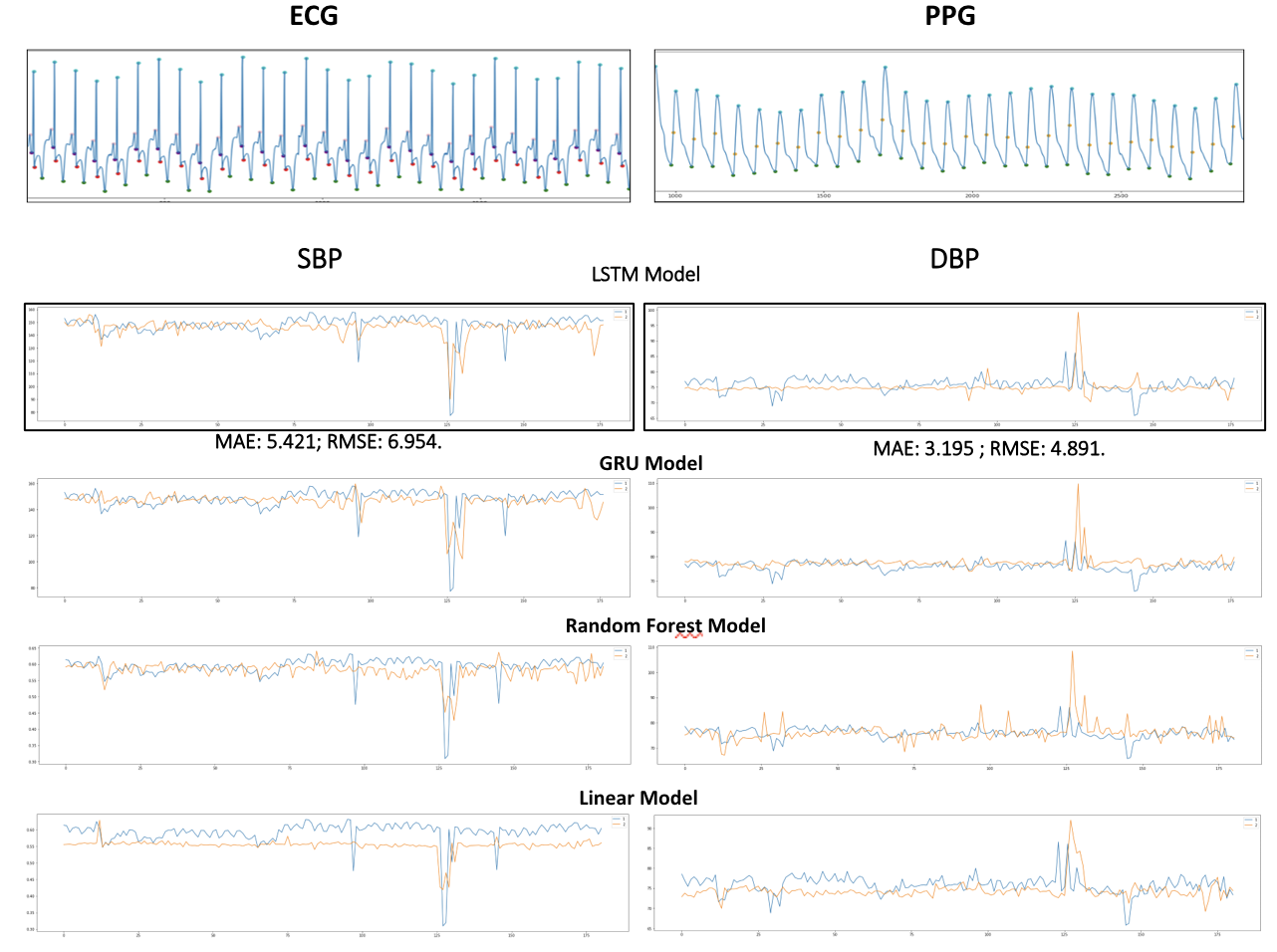
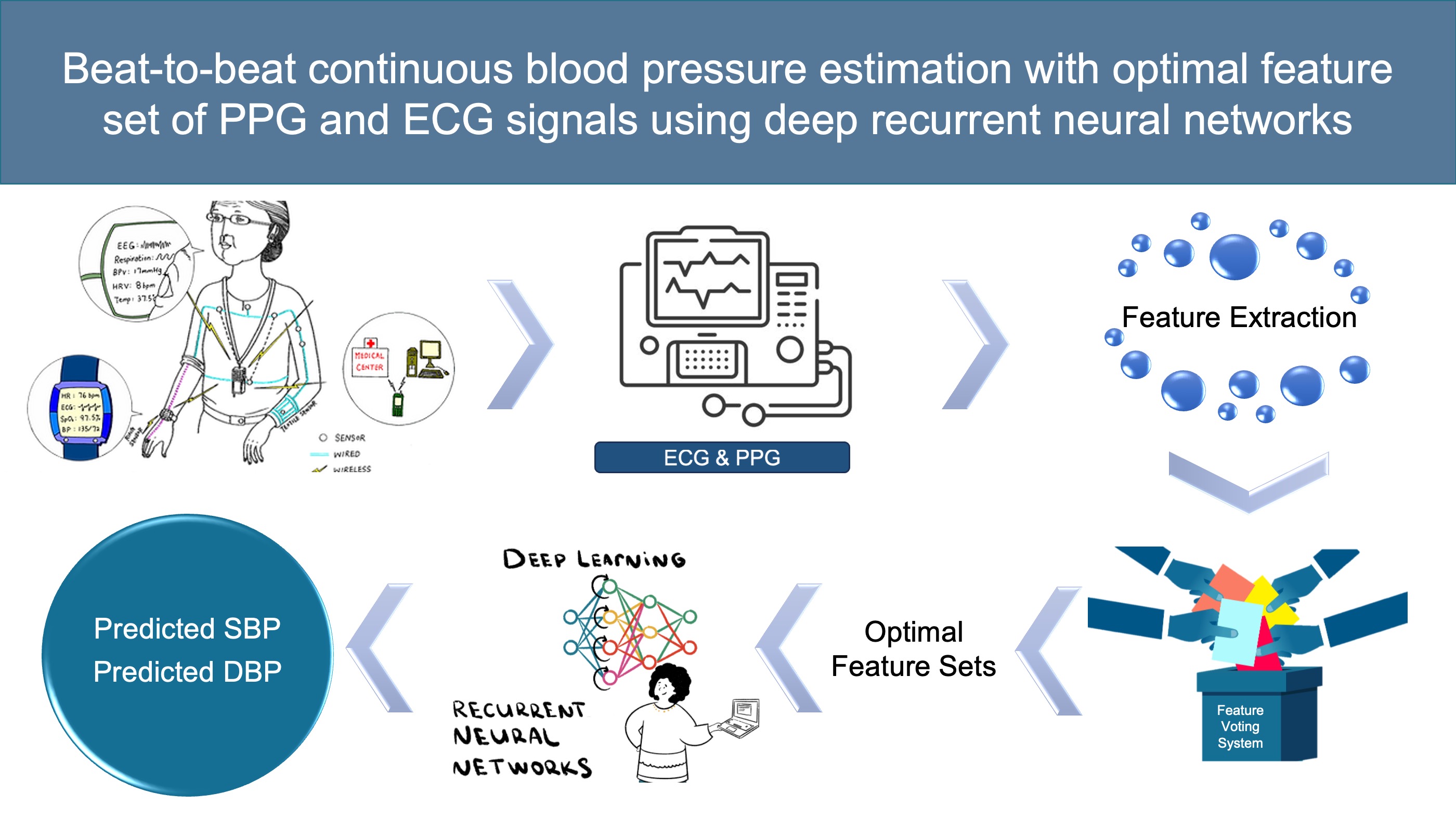
Beat-to-beat continuous blood pressure estimation with optimal feature set of PPG and ECG signals using deep recurrent neural networksChen H, Lyu L, Zeng Z, Jin Y, Zhang Y Vessel Plus, 2023 paper / Deep RNN for continuous BP estimation using PPG and ECG. Achieved MAE of 2.514 and 1.383 mmHg for SBP/DBP on 660 subjects, attaining grade A per BHS standards. |
|
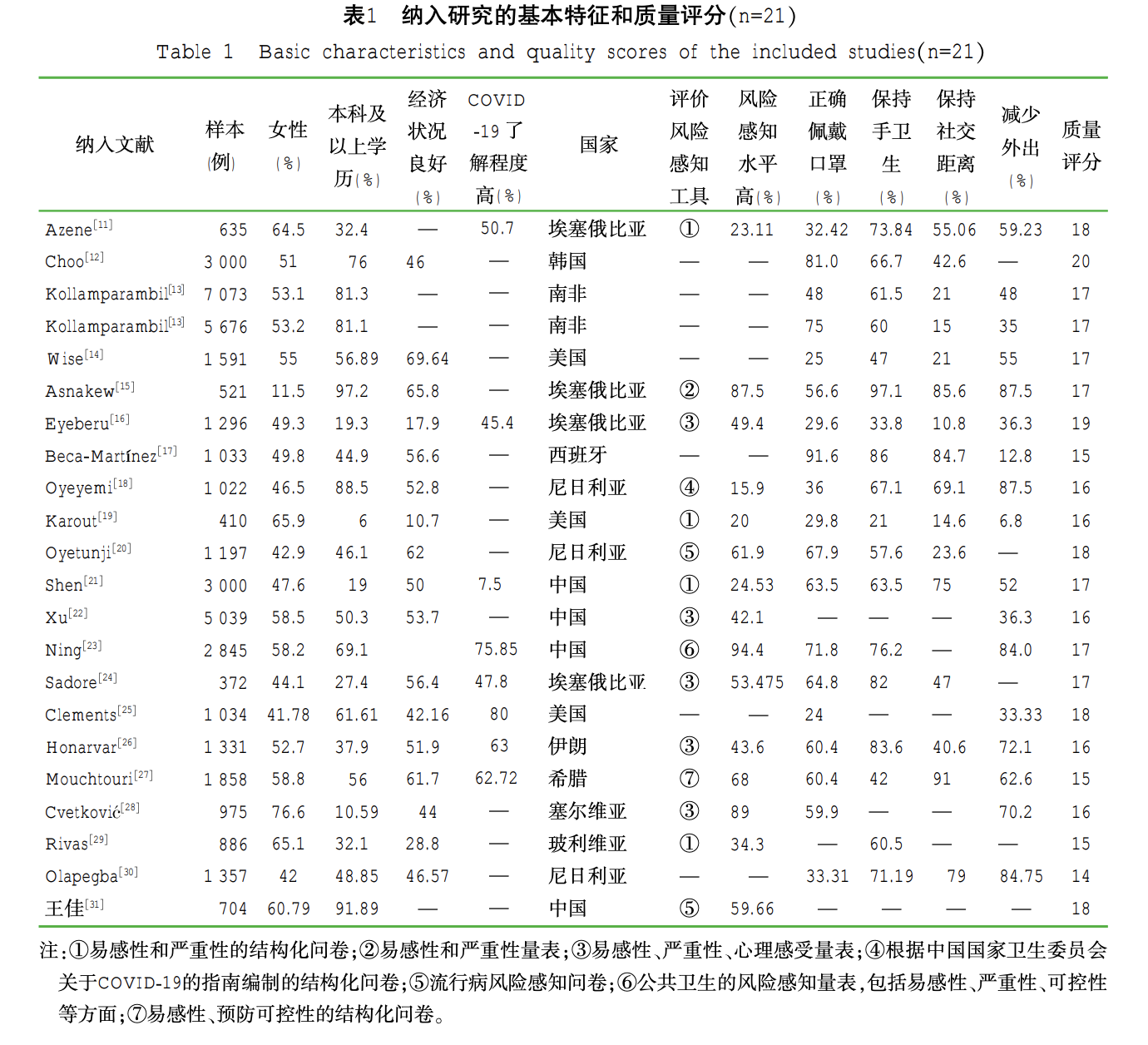
Public risk perceptions and coping behaviors in novel coronavirus pneumonia outbreaks: a systematic reviewJin YW, Sun HY, Ji Y Chinese Journal of Nursing Education, 2023 paper / Systematic review of 21 studies (42,855 participants) on public risk perception during COVID-19. Found 51.1% had high-level risk perception. |
|
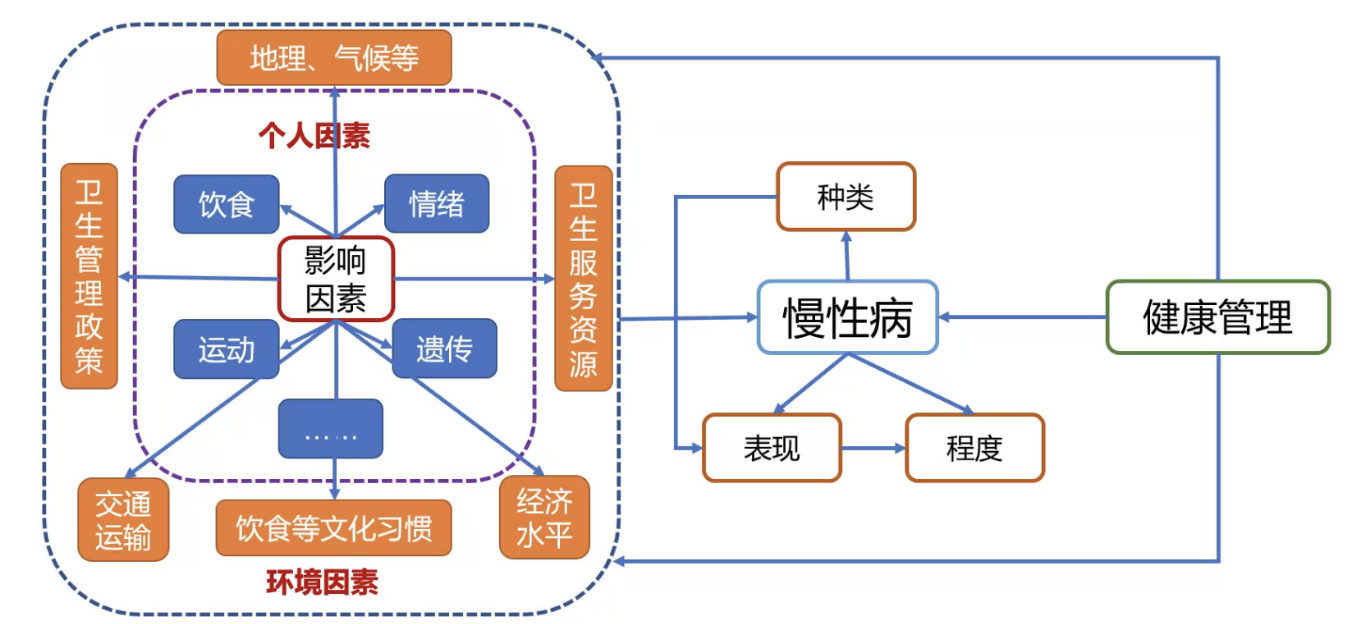
Evolution of risk perception of medical staff during public health emergencies: a qualitative studyLi YQ, Gu JN, Sun YM, Shao J, Dang Y, Guo JM, Jin YW, Hu GY, Sun HY Modern Clinical Nursing, 2022 paper / Qualitative study on medical staff risk perception evolution during public health emergencies. Identified three stages: Vigilance, Observation, and Maintenance. |
|
Modified version of template from here |